
Polymer Horizontal Line Post Insulator
- Information
- Product Description
Polymer Horizontal Line Post Insulator

33kV Line Post Insulator

66kV Line Post Insulator

132kV Line Post Insulator

220kV Line Post Insulator
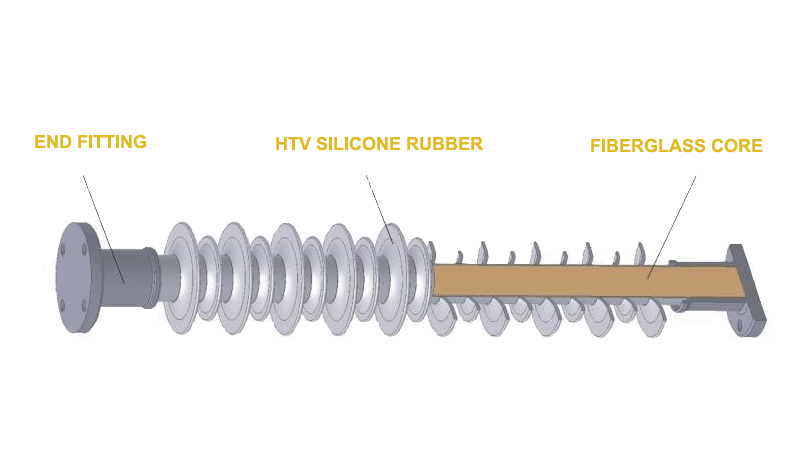
Brief Intruction
Composite line post insulator, also known as polymeric line post insulator, is an insulator widely used in electrical transmission and distribution lines. Polymer line post is mainly made of three parts, which gives the polymer line post unique characteristics and advantages over traditional porcelain insulators.
Fiberglass core
HTV silicone rubber
Metal end fittings.
The key characteristics of horizontal line post insulators include high mechanical strength, superior electrical performance, lightweight design, and pollution resistance. These features make them a reliable and efficient choice for insulating transmission and distribution lines, ensuring the smooth and safe operation of electrical systems.
About Us

Key Features
High mechanical strength. The FRP core provides excellent load-bearing capability, allowing the insulator to withstand various mechanical stresses, such as wind, ice, and vibration. This makes them highly suitable for use in areas with harsh weather conditions or high mechanical loads.
Lightweight design. Compared to traditional porcelain insulators, the horizontal line post insulators are significantly lighter, making installation and maintenance easier, and more cost-effective. Additionally, the lightweight construction reduces the load on supporting structures, improving the overall stability of the transmission lines.
Excellent resistance to pollution. The hydrophobic nature of the silicone rubber housing prevents the accumulation of dirt, dust, and pollutants on the surface, reducing the risk of flashovers caused by pollution. This makes them particularly suitable for use in coastal areas or regions with high levels of industrial pollution.
Technical Data Sheet
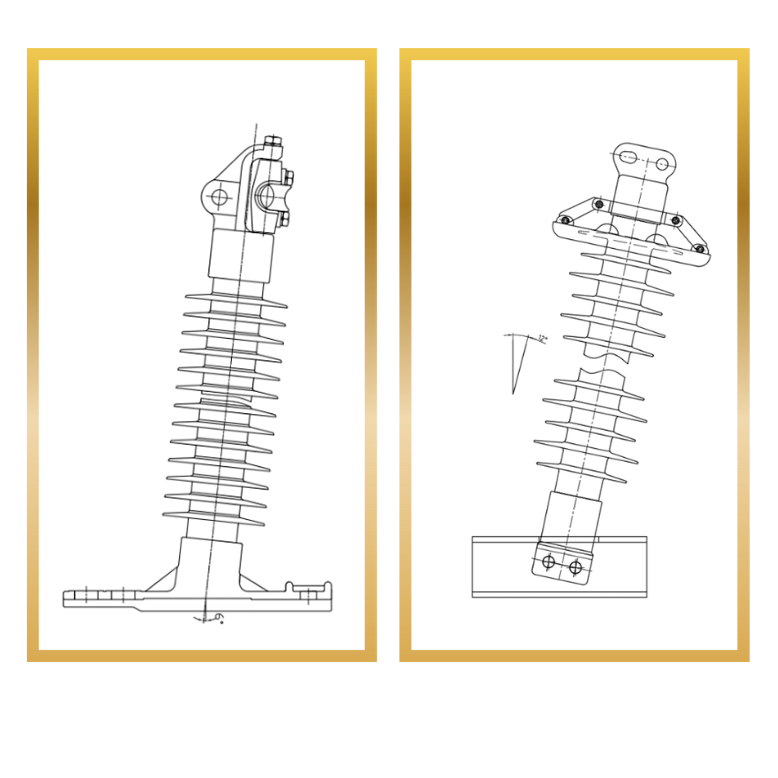
Composite horizontal line post insulator
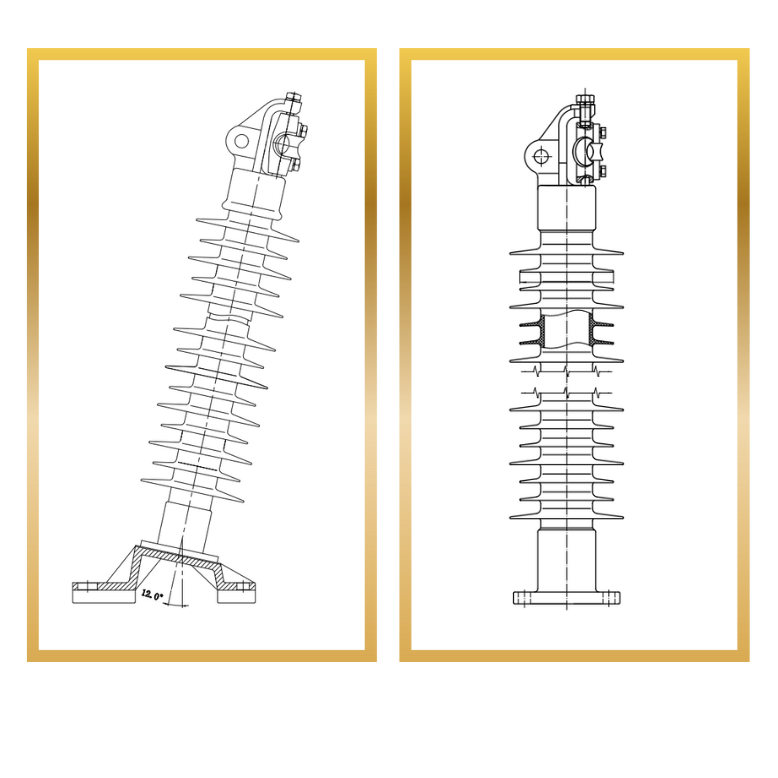
Polymer horizontal line post insulator
| Drawing No. | Rated voltage (kV) | Section length (mm) | Cantilever strength (kN) | Creepage distance (mm) | Lightning impulse withstand voltage (kV) | Power frequency withstand voltage (kV) |
| FPW-11/10 | 11 | 225 | 10 | 300 | 130 | 48 |
| FPW-33/10 | 33 | 387 | 10 | 900 | 200 | 100 |
| FZS-69/11.1 | 69 | 950 | 11 | 1753 | 260 | 130 |
| FZSW-138/10 | 138 | 1661 | 101 | 4495 | 700 | 400 |
| FZSW-230/12.5 | 230 | 2278 | 12.5 | 7200 | 1050 | 460 |
Composite Line Post Insulator Standard
Insulators for overhead lines – Composite line post insulators for AC systems with a nominal voltage greater than 1 000V –
American National Standard for Composite Insulators—Transmission Line Post Type
American National Standard for Composite Insulators—Distribution Line Post Type
Composite Line Post Insulator Workshop
Three Ways of Manufacturing
1
Compression Molding
The molding method is normally used for low or medium voltage insulators
2
Injection Molding
injection molding technology is used for vulcanization of the silicone shed to the high voltage insulators.
3
Modular Approach
Allows for a wider range of possible shed geometries,insulator designs, without a corresponding large investment in different costly mold

Semi-Finished Insulators
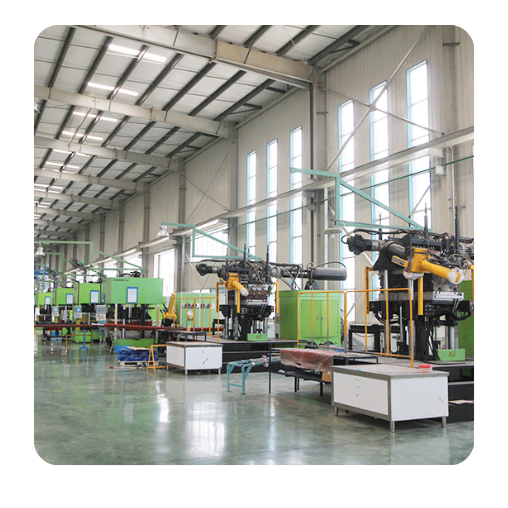

Workshop
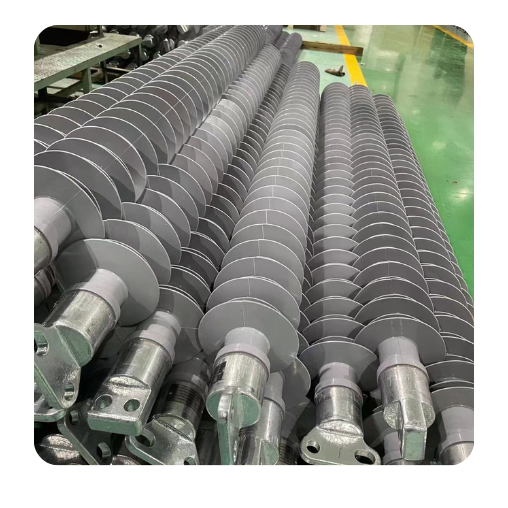

HV Line Post Insulators
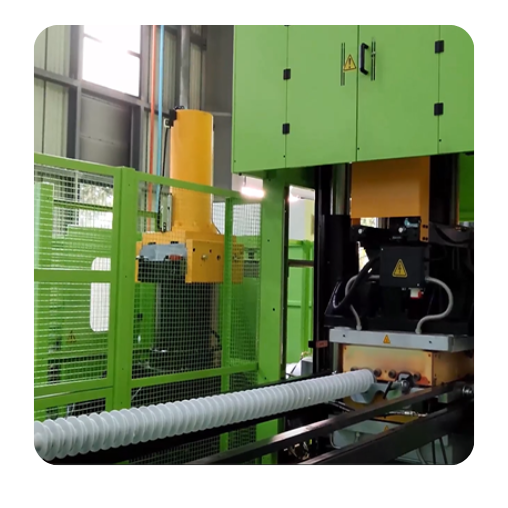

In Process

Semi-Finished Insulators

Workshop

HV Line Post Insulators

In Process
Test Facilities
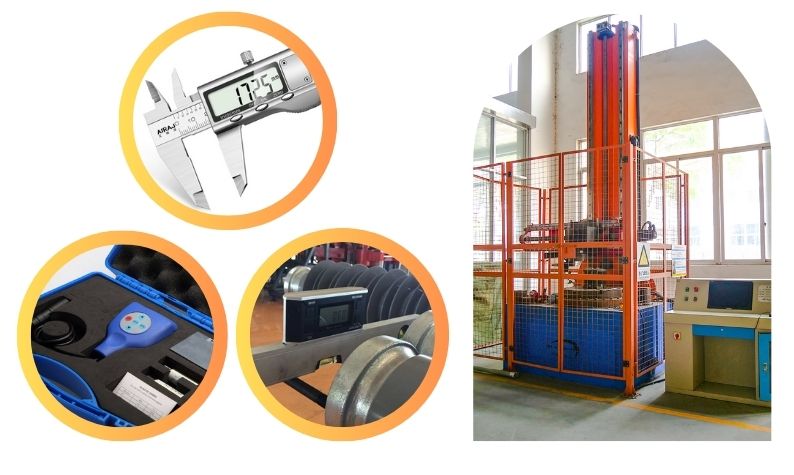

Dimensional Check & Bending Load Test
- Visual examination
- Verification of dimensions (E1+E2)
- Galvanizing test (E1+E2)
- Verification of the SCL (E1)
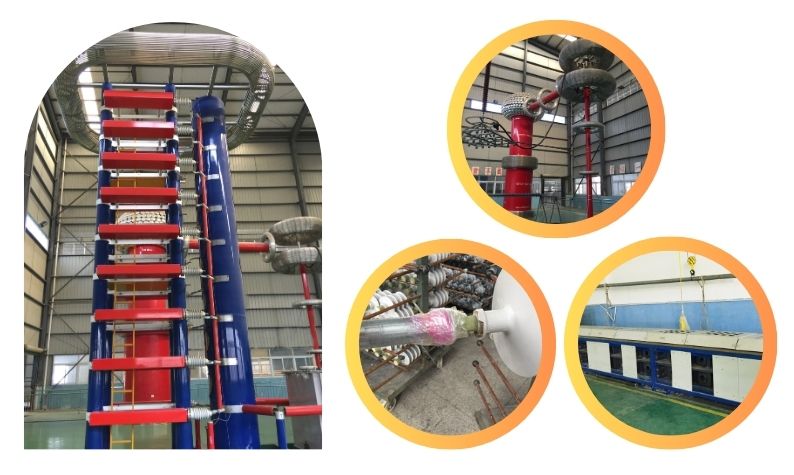

Electrical & Tension Load Test
- Dry lightning impulse withstand voltage test
- Wet power frequency test
- Wet switching impulse withstand voltage test for insulators intended for systems with
Um≥300kV
- Tension load test
Polymer Line Post Packing & Delivery
Sea-Worthy & Air-Worthy Packing Solution
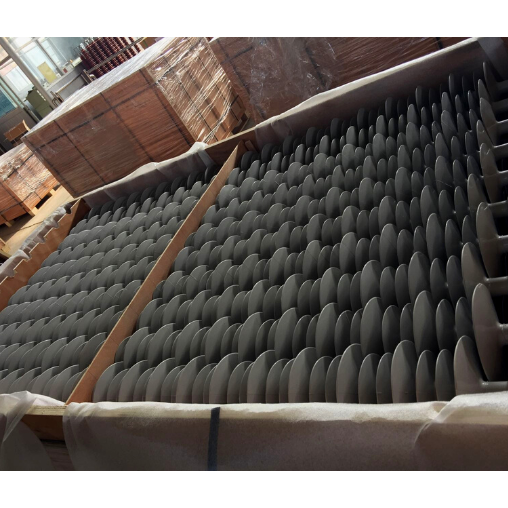

PLYWOOD CASE
Free from fumigation, plywood cases offer a combination of strength, durability, customizability, and cost-effectiveness, making them a reliable and efficient packaging solution for a wide range of industries.
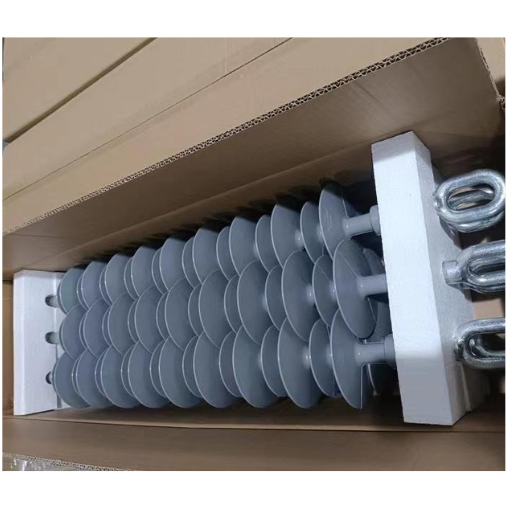

carton BOX
Cartons come in various shapes and sizes, making insulators suitable for packaging a wide range of products, lightweight and stackable, easy for storage and transportation. Recyclable materials, Cost-effective
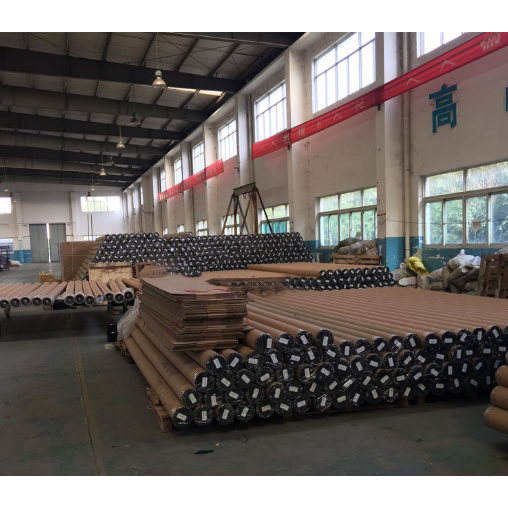

PAPER TUBE
Suitable for pack the high voltage long rod suspension insulators, or composite line post insulators, and composite station post insulators. Costly but better performance comparing to plywood case and cartons.
Line Post Insulator Application
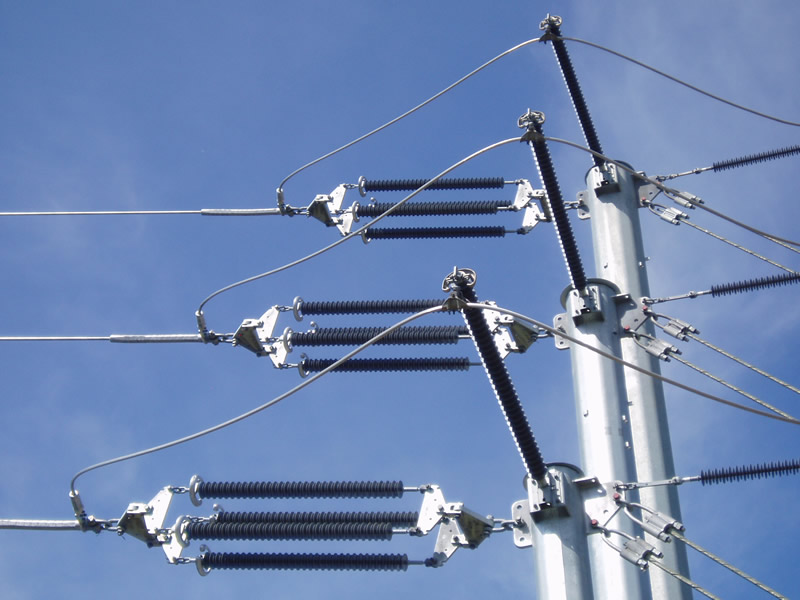

Horizontal line post insulators are used in electrical power transmission and distribution systems to support and insulate overhead power lines. They are typically made of ceramic or composite materials and have a cylindrical shape with a horizontal orientation.
The main application of horizontal line post insulators is to provide electrical insulation and mechanical support for power lines, preventing current leakage and ensuring the safe and reliable transmission of electricity. These insulators are designed to withstand high voltage levels and various environmental conditions, such as rain, humidity, and pollution.
Horizontal line post insulators are installed on transmission and distribution poles or towers, with the power line passing through the center hole of the insulator. The insulator's surface is designed to prevent the formation of a conductive path between the power line and the pole or tower, thereby preventing electrical arcing and flashovers.
In addition to their insulation properties, horizontal line post insulators also provide mechanical support to the power lines. They are designed to withstand the mechanical stresses caused by wind, ice, and other environmental factors, ensuring that the power lines remain stable and secure.
Overall, braced insulators play a critical role in maintaining the reliability and safety of overhead power transmission and distribution systems. They provide both electrical insulation and mechanical support, allowing for the efficient and uninterrupted transmission of electricity.
Core of a composite insulator
The internal insulating part of a composite insulator which is designed to ensure the
mechanical characteristics. The core usually consists of either fibres which are positioned in a resin-based matrix or a homogeneous insulating material.














