
Composite Long Rod Insulator
- Information
- Product Description
- Video
Composite Long Rod Insulator Introduction
1. Composite insulator structure
The composite insulators have a core, housing & weather shed of insulating material and steel/aluminum alloy hardware components for attaching the silicone rubber insulators to the
support/conductor.
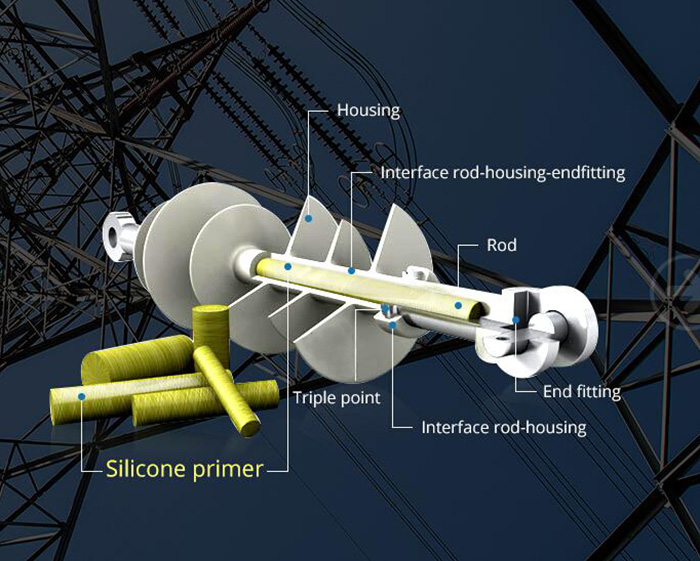

1) Core: Composite long rod insulator core is a glass-fiber reinforced epoxy resin rod of high strength (FRP rod). Glass fibers and resin are optimized in the FRP rod. Glass fibers are Boron free electrically corrosion resistant (ECR) glass fiber or Boron free E-Glass and exhibit both high electrical integrity and high resistance to acid corrosion. The matrix of the FRP rod should be Hydrolysis resistant. The FRP rod should be manufactured through a Pollution process. The FRP rod is void free.
2) Housing (Sheath): The FRP rod is covered by a seamless sheath of a silicone electrometric compound or silicone alloy compound of a thickness of 3mm minimum. The silicone rubber insulator shed should protect the FRP rod against environmental influences, external pollution, and humidity. The composite insulator is extruded or directly molded on the core and has chemical bonding with the FRP rod. The strength of the bond is greater than the tearing strength of the polymer. Sheath material in the bulk as well as in the sealing/bonding is free from voids.
3) Weather sheds: The composite polymer weather sheds made of silicone electrometric compound or silicon alloy are firmly bonded to the sheath, vulcanized to the sheath, or molded as part of the sheath and shall be free from imperfections. The weather sheds should have silicon content of a minimum of 30% by weight. The strength of the weather shed to the sheath interface is greater than the tearing strength of the polymer. The interface, if any, between sheds and sheath (housing] is free from void
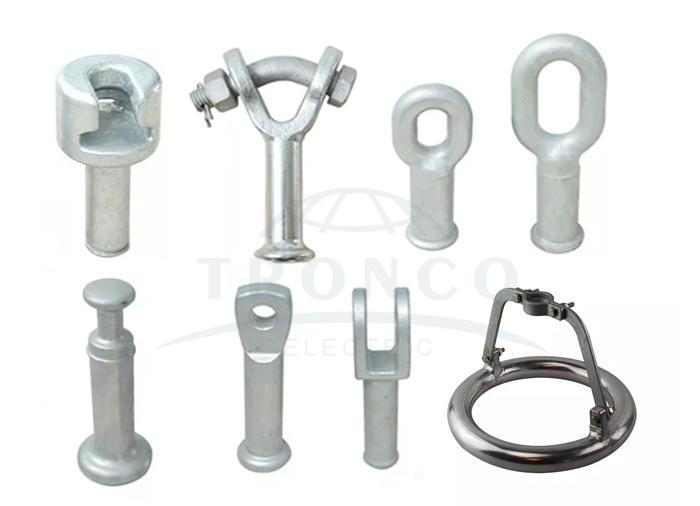
4) End Fittings: Composite long rod insulator end fittings transmit the mechanical load to the core. The fittings are made of spheroidal graphite cast Iron, malleable cast iron, or forged steel or aluminum alloy. Fittings are connected to the rod by means of a controlled compression technique. The gap between the fitting and sheath is sealed by a flexible silicone electrometric compound or silicone alloy compound sealant. The system of attachment of end fitting to the rod provides a superior sealing performance between housing, i.e. seamless sheath and metal connection. The sealing must be moisture-proof.
2. Technical specifications
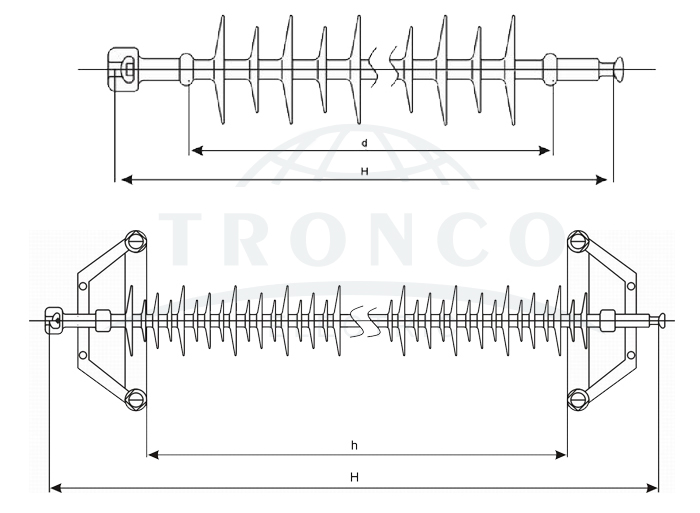
No. |
Type | Rated voltage KV | Specified mechanical failing load KN | Coupling size | Lightning impulse withstand voltage ≥ (kV) | Wet power frequency voltage ≥ (kV) |
1 | FXBW-11/70 | 11 | 70 | 16 | 95 | 38 |
2 | FXBW-33/70 | 33 | 70 | 16 | 170 | 70 |
3 | FXBW-66/120 | 66 | 120 | 16 | 350 | 140 |
| 4 | FXBW-110/70 | 110 | 70 | 16 | 650 | 280 |
| 4 | FXBW-110/120 | 110 | 120 | 16 | 650 | 280 |
| 5 | FXBW-132/70 | 132 | 70 | 16 | 650 | 320 |
| 6 | FXBW-132/120 | 132 | 120 | 16 | 650 | 320 |
| 7 | FXBW-220/120 | 220 | 120 | 16 | 1050 | 450 |
| 8 | FXBW-220/160 | 220 | 160 | 20 | 1050 | 450 |
| 9 | FXBW-330/160 | 330 | 160 | 20 | 1175 | 520 |
| 10 | FXBW-330/210 | 330 | 210 | 20 | 1175 | 520 |
| 11 | FXBW-400/160 | 400 | 400 | 20 | 1550 | 625 |
| 12 | FXBW-400/210 | 400 | 400 | 20 | 1550 | 625 |
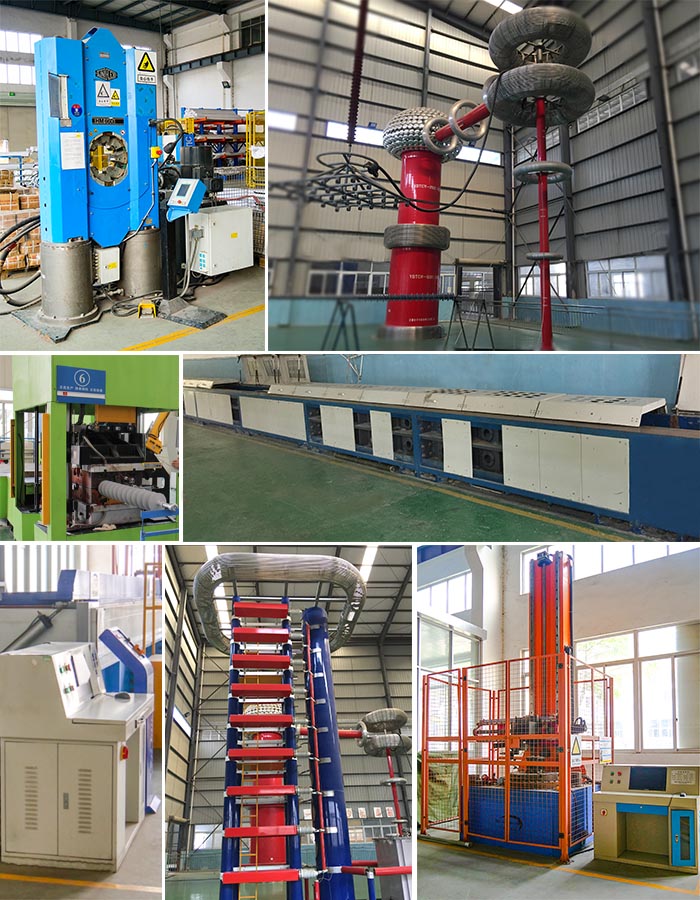
3. Manufacture process
Preparation process
Raw material mixing process
Core rod and metal fitting assembly process
Injection molding process
Flash-removing process
Metal fitting crimping process
Routine test & Sample test
Packing and delivery

4. Inspection
The polymer insulators for final inspection are offered by Shenyang Tronco Electric Co., Ltd only under packed conditions. The client can select the samples at random from the packed lot for carrying out acceptance tests. Tronco Electric keeps the client informed in advance of the time of starting and the progress of the manufacture of insulators in the various stages so that arrangements can be made for inspection.
The sample test is to be performed according to IEC61109 for composite long-rod insulators.
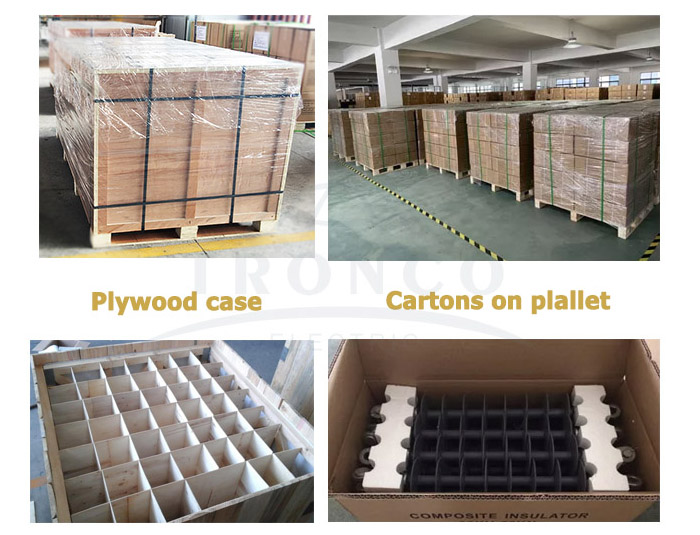
5. Packing and shipment
Composite polymer insulators can be packed in carton boxes, plywood cases, and paper tubes (over 230kV long rod insulators).
6. Applications of Composite Insulators in Power Transmission and Distribution Systems
Silicone rubber insulator, also called FRP insulator, is widely used for power systems with the advantages of small volume, light weight, convenience for transportation and installation, good corrosion resistance, aging resistance, electrical and mechanical properties, excellent hydrophobicity, and migration.
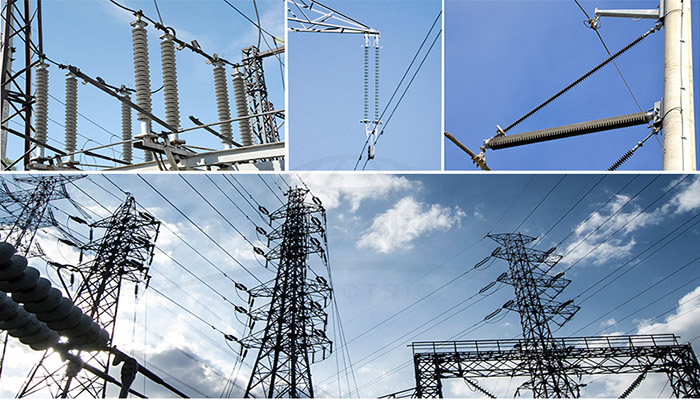

Power Transmission Lines: Composite insulators play a crucial role in overhead power transmission lines, especially in areas with high pollution, coastal regions, or areas prone to industrial contaminants. These insulators are highly valued for their exceptional pollution performance and hydrophobicity. By preventing flashovers, they significantly improve the reliability and efficiency of transmission lines.
Distribution Lines: Composite insulators are also extensively used in distribution lines, which are responsible for delivering electricity from substations to residential, commercial, and industrial areas. They provide insulation and mechanical support to the conductors, ensuring safe and reliable power distribution.
Substations: In substations, composite insulators insulate bus bars, transformers, circuit breakers, and other equipment. One of the key advantages of these insulators is their lightweight nature, which makes handling and installation easier. Furthermore, they offer excellent resistance to cracking, corrosion, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation, guaranteeing long-term performance in even the most demanding outdoor environments.
Railway Electrification: Composite insulators find wide application in railway electrification systems, providing insulation and support for overhead catenary wires. Their low weight, high mechanical strength, and resistance to vandalism make them highly suitable for railway infrastructure projects.
Industrial Applications: Various industrial applications, such as power plants, petrochemical plants, and manufacturing facilities, rely on composite insulators for reliable insulation and support in high-voltage equipment, switchgear, and control systems. These insulators ensure the safe and efficient operation of these facilities.
Renewable Energy Projects: Composite insulators are increasingly being utilized in renewable energy projects, including wind farms and solar power plants. Their resistance to environmental factors, such as UV radiation, humidity, and temperature variations, ensures reliable performance in harsh outdoor conditions.
High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission: Composite insulators are well-suited for HVDC transmission systems, which are used to transmit large amounts of electricity over long distances. They provide reliable insulation and mechanical strength in HVDC converter stations, smoothing stations, and transmission lines.
Mechanical failing load from 10kV to 500kV.
Line voltage from 10kV to 300kN.
End fitting connection: ball & socket; tongue & clevis; Y-clevis & ball; Oval eye & ball; etc...
Composite long rod insulator has good performance of anti-bending, anti-pollution, anti-shock, and anti-brittle. With its small size and lightweight, good self-cleaning properties, the composite insulator can be installed conveniently. And the composite insulator is interchangeably compared to porcelain products.














