
10 Types of Insulators Used in Power Transmission Lines
2022-11-07 22:05The following are the main types of insulators used in power transmission lines:
1. Disc Insulators
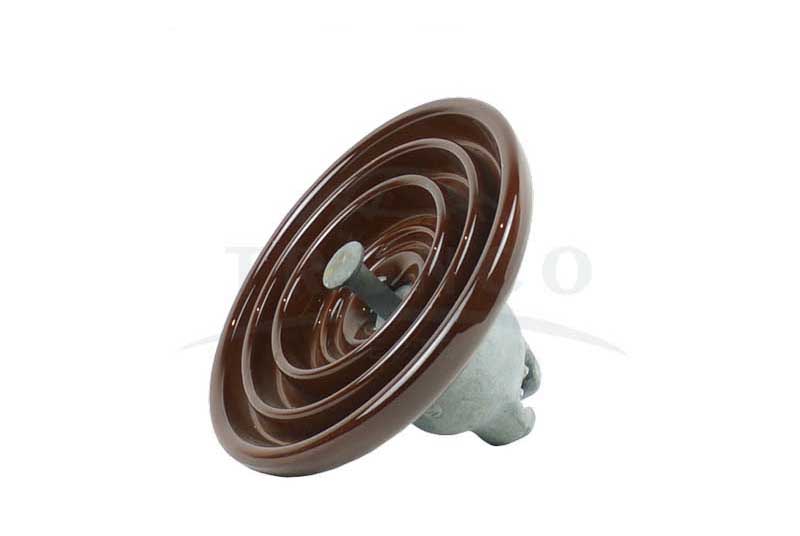

As the name suggests, the shape of the insulator is like a disc hence it is called a disc insulator. These types of insulators are used in high-voltage transmission and distribution lines. Disc insulators are designed to meet the required electro-mechanical strength.
In addition, they are a cost-effective solution for medium and low-polluted environments. The applications of these insulators include transmission lines, industrial and commercial as they have highly efficient features like low corrosion, and robust design. They provide insulation as well as support to line conductors in suspension and tension systems. Also, it is capable of maintaining high voltages within high loads.
2. Post Insulators
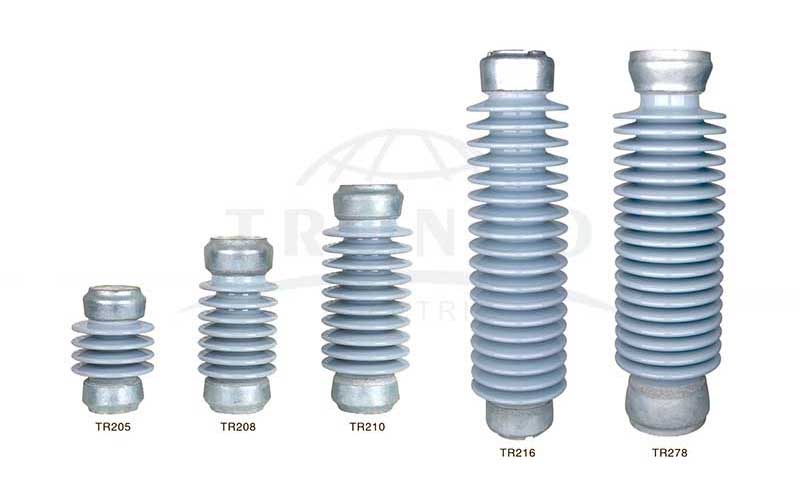

It is a high-voltage insulator designed to be used in substations because it is suitable for different voltage levels. These are employed because they ensure the safe and stable distribution of electricity generated in power plants. Post-insulators are made of ceramic material or of a single piece of composite material (silicone rubber) and are capable of carrying power up to 1100KV. It is placed in a vertical position and is widely used to protect transformers, switchgear, and other connecting equipment due to its excellent mechanical properties.
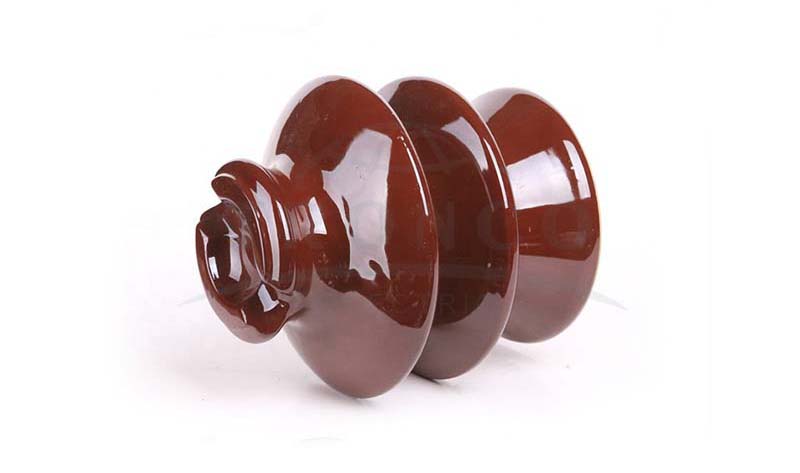
3. Pin Insulators

![]()
The pin insulators are mostly seen in power distribution lines. It is a device that insulates a wire from physical support such as a pin (wooden or metal dowel) on a utility pole. It is a single-layer shape made of a non-conducting material, usually porcelain or glass. Single or number of pin insulators can be used on physical support, depending on the application of voltage. The pin insulator is capable of carrying voltages up to 11kV and is designed with a high mechanical strength material. These are arranged in either a vertical or a horizontal position.
4. Strain Insulators
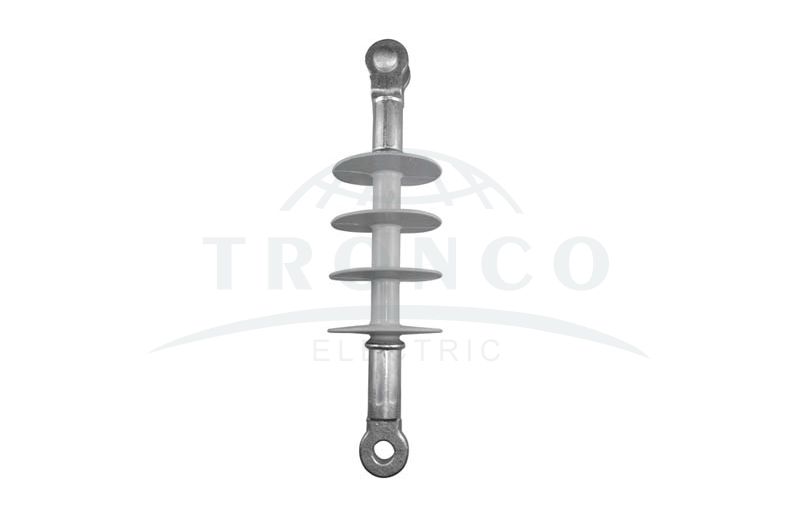
These types of insulators are designed to operate under mechanical stress to withstand the stretch of a suspended electrical wire or cable. It is similar to a suspension insulator as it is used to support radio antennas and overhead power lines. A strain insulator is arranged between two lengths of wire to electrically separate them from each other while maintaining a mechanical connection. Or used where a wire joins a pole or tower, to deliver the pull of wire to support while electrically insulating it. These insulators have a voltage potential of about 33kV.
5. Suspension Long Rod Insulators
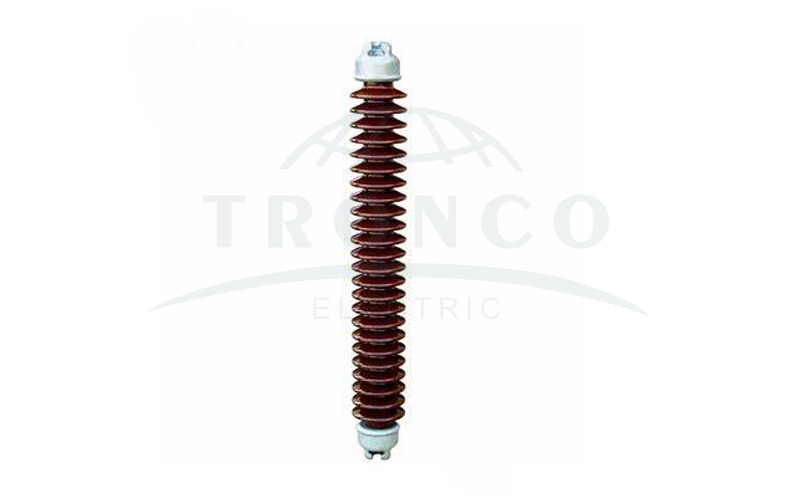

These types of insulators are generally used as conductors to protect the overhead transmission lines. The suspension insulator is commonly made of porcelain material and is used in towers. They have a number of insulators that are connected in series to a form string. It is hinged on the cross arm of the tower and carries a power conductor at its lowest end. These are used where a higher voltage of about 33 kV is required. Pin insulator becomes economical as the size, and weight of the insulator becomes more. To overcome these difficulties, a suspension insulator is used.
6. Shackle Insulators
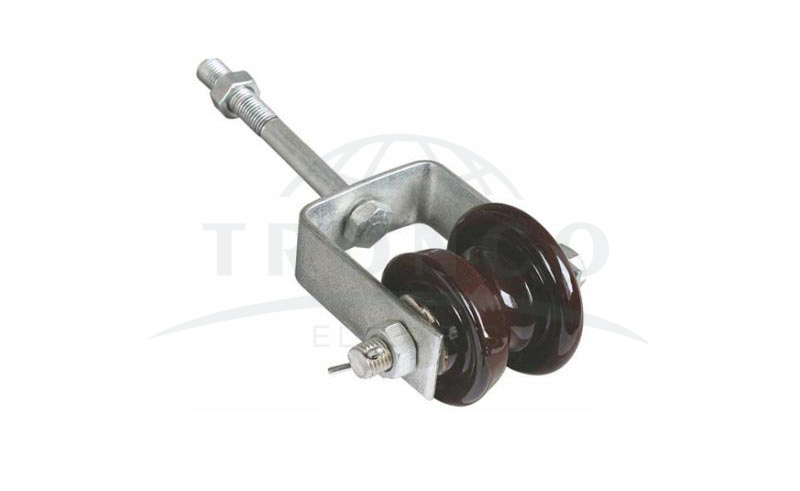

Shackle insulators are generally small in size and used in low-voltage distribution systems. This type of insulator can be used in both vertical and horizontal positions. The connection of this insulator can be done using a metal strip and is capable of carrying a voltage of about 33 kV. It has a tapered hole that distributes the load force more consistently, reducing the chance of fracture once heavily loaded. The use of insulators has decreased recently after the widespread use of underground cables for distribution purposes.
7. Stay Insulators
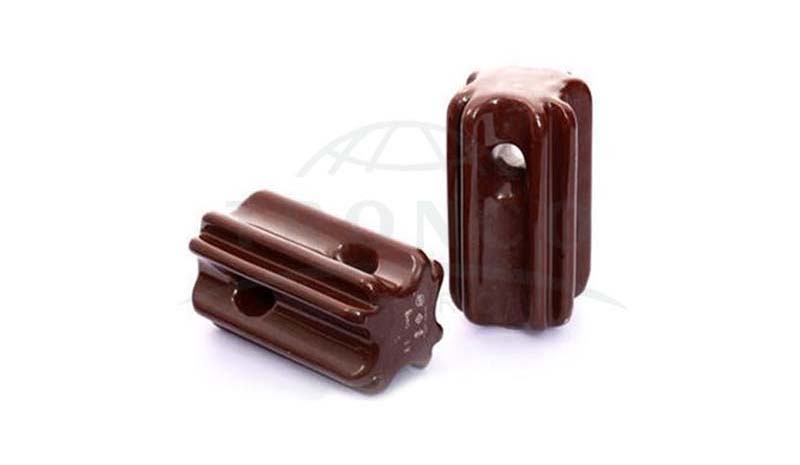

It is a type of low-voltage insulator designed to counterweight and fasten dead-end poles by combining a stay wire or main grip. These insulators are rectangular in shape and are available in smaller sizes than other types. These insulators can be arranged between the line conductor and the earth. In addition, they also act as protection devices that protect against sudden faults and otherwise sudden voltage changes. The importance of these insulators is seen when the poles fall to the ground or when the stay wires are accidentally broken due to additional mechanical load.
8. Polymer Post Insulators
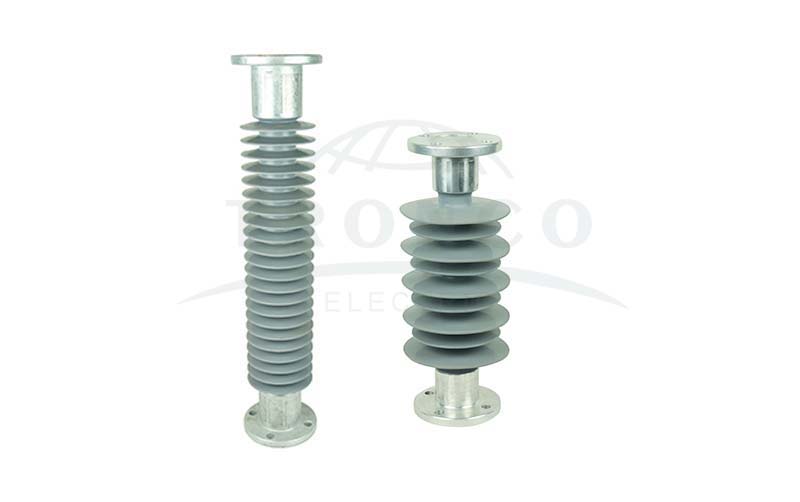

These are a type of electrical equipment usually made of polymer materials and metal fittings. Furthermore, these insulators are made of fiberglass rods and are surrounded by polymer weather sheds. Weather shades shield the insulator core from the outer environment. Polymer insulators are lighter in weight than the porcelain type while providing better power. In general, it is considered a good insulator for both heat and electricity. It is used as an insulator due to its unique electrical, mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties.
9. Glass Insulators
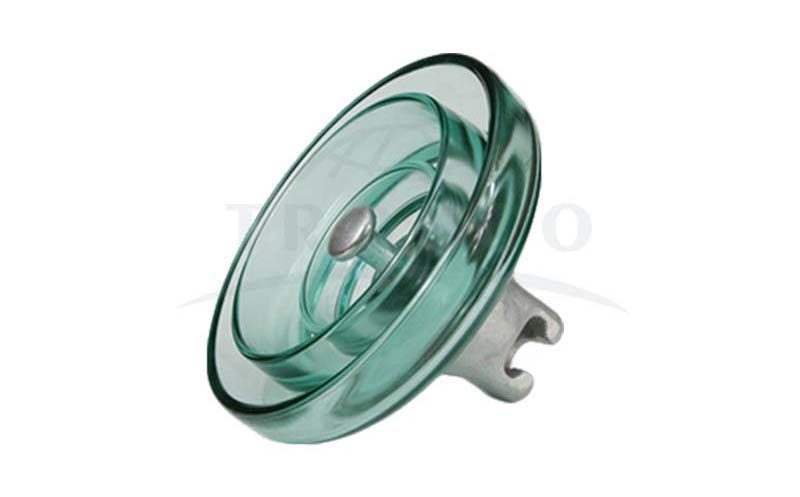

These are types of insulators used in power transmission lines that are usually made of annealed or toughened glass. The purpose of this insulator is to insulate the electrical wires, so that electricity does not leak into all the poles and into the earth. Previously, glass insulators were used in telegraph and telephone lines, which were later replaced by ceramic and porcelain types in the 19th century. To overcome the weakness of the glass, toughened glass types were introduced, which became popular due to their long life span.
10. Long Rod Insulators
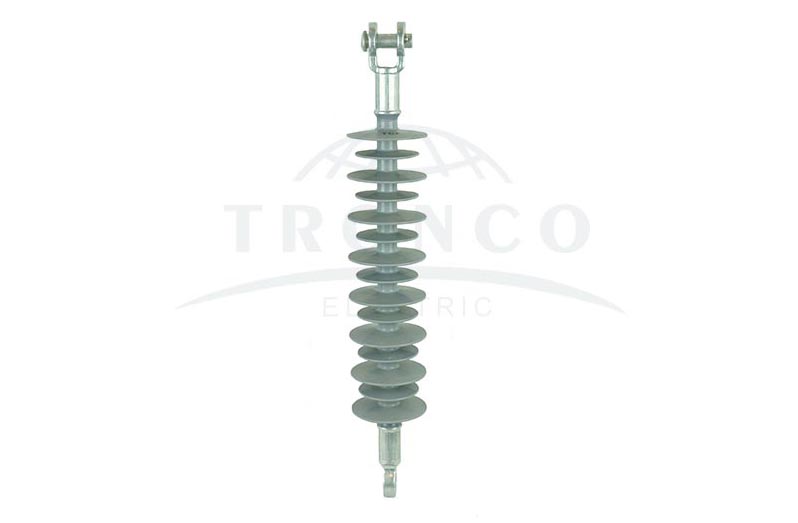

The long rod insulators are usually hinged on steel towers to insulate the transmission lines. In addition, they also act as protection devices as they supply power safely. Depending on the use and requirement, long rod insulators are generally composed of multiple insulators. These are porcelain rods with weather shed and metal end fittings on the outside. The advantage of employing this type of insulator is that they are applicable for use in both tension and suspension locations.
